
(a)
Interpretation:
Product formed during the reaction of given anhydride with the given reagent has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(b)
Interpretation:
Product formed during the reaction of given anhydride with the given reagent has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(c)
Interpretation:
Product formed during the reaction of given anhydride with the given reagent has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction:
LAH Reduction: The saturated/unsaturated aldehyde and ketones in the presence of sodium metal in LAH and carbonyl compound produced saturated alcohols. The keto group involves in the reduction process of LAH, this end up reducing to give the alcohols.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of
(d)
Interpretation:
Product formed during the reaction of given anhydride with the given reagent has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
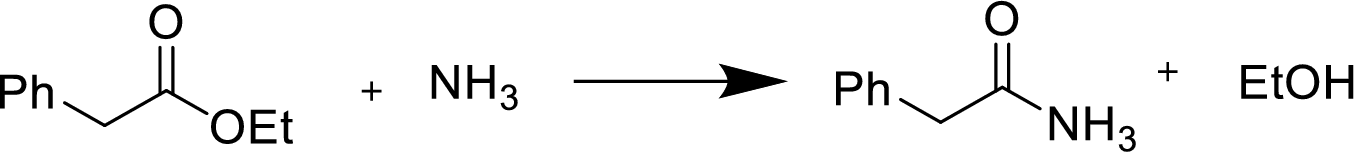
(e)
Interpretation:
Product formed during the reaction of given anhydride with the given reagent has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of an ester with ammonia or an
Treatment of an ester with ammonia or a primary or secondary amine gives an amide.
The nucleophilic addition of the ammonia or amine to the carbonyl carbon occurs followed by a proton transfer and a tetrahedral addition intermediate is formed. The intermediate can directly alkoxide and lose a proton to the alkoxide to give products.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Fill in the missing starting material by drawing a specific compound that would complete this reaction with the listed reagents.arrow_forwardUse any needed reagents to effect the following transformationarrow_forwardCould you help show the reagent and the synthetic intermediates to the product?arrow_forward
- Which routes could be used to synthetize the product in the center?arrow_forwardShow a mechanism for the conversion of any aldehyde or ketone and any alcohol (as solvent) to the acetal with added gaseous HCL as the catalystarrow_forwardProvide the product or reagent that completes each of the given transformationsarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
