
Concept explainers
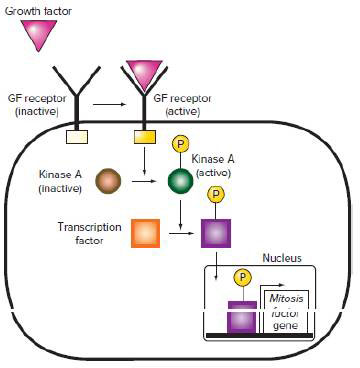
A generic signaling cascade is shown in the following figure. A growth factor (GF) binds to a growth factor receptor, activating the kinase function of an intracellular domain of the growth factor receptor. One substrate of the growth factor receptor kinase is another kinase, kinase A, that has enzymatic activity only when it is itself phosphorylated by the GF receptor kinase. Activated kinase A adds phosphate to a transcription factor. When it is unphosphorylated, the transcription factor is inactive and stays in the cytoplasm. When it is phosphorylated by kinase A, the transcription factor moves into the nucleus and helps turn on the transcription of a mitosis factor gene whose product stimulates cells to divide.
| a. | The following list contains the names of the genes encoding the corresponding proteins. Which of these could potentially act as a proto-oncogene? Which might be a tumor-suppressor gene?
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Though it is not pictured, the cell in the figure also has a phosphatase, an enzyme that removes phosphates from proteins—in this case, from the transcription factor. This phosphatase is itself regulated by kinase A. | |||||||||||||||||||
| b. | What would you expect to be the effect when kinase A adds a phosphate group to the phosphatase? Would this activate the phosphatase enzyme or inhibit it? Explain. | ||||||||||||||||||
| c. | Is the phosphatase gene likely to be a proto-oncogene or a tumor-suppressor gene or neither? | ||||||||||||||||||
| d. | Several mutations are listed below. For each, indicate whether the mutation would lead to excessive cell growth or decreased cell growth if the cell were either homozygous for the mutation, or heterozygous for the mutation and a wild-type allele. Assume that 50% of the normal activity of all these genes is sufficient for normal cell growth.
|
||||||||||||||||||
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Which of the following statements is FALSE? The mammalian glucocorticoid receptor: awaits the steroid hormone at the cell surface and is internalized into the cytoplasm upon glucocorticoid binding. is a hormone-dependent transcription factor. may act as an activator or repressor of transcription depending on the promoter it acts on. is sequestered in the cytoplasm by HSP90 as long as the glucocorticoid is absent. does not require phosphorylation by protein kinase A to bind DNA.arrow_forwardCancers are often caused by overactive growth factor receptor signaling (remember growth factor receptors are enzyme-linked receptor pathways). If you were able to use gene therapy to overexpress a particular protein in a cancer cell, which of the following might be useful to overexpress in order to combatt cancer? a GAP that acts on Ras a phosphatase that acts on GPCR a protein that enhances the activity of Akt a ubiqtuin ligase that acts on the MAPK phophatasearrow_forwardwhich of hthe following would result in a persisting proliferation response to growth factor receptor activation after the ligand is no longer binding to its rceptor kinase? 1. Both a mutation that blocks the GTPas activity of Ras and a mutation that blocks the exchange of GDP with GTP would cause the response to persist. 2. a mutation that blocks the GTPas activity of Ras 3. neither a mutation that blocks the GTPas activity of Ras nor a mutation that blocks the exchange of GDP with GTP would cause the response to persist 4. a mutatiaon that blocks the exchange of GDP with GTParrow_forward
- Tumor cells from a person with leukemia have been analyzed to determine which oncogene is involved in the transformation. After partial sequencing of the gene, the predicted gene product is identified as a tyrosine kinase. Which of the following proteins would most likely be encoded by an oncogene and exhibit tyrosine kinase activity? A. Nuclear transcriptional activator B. Epidermal growth factor C. Membrane-associated G protein D. Platelet-derived growth factor E. Growth factor receptorarrow_forwardEven in the presence of a Ras-GAP, a single amino acid change in as renders it incapable of hydrolyzing GTP. This mutation is known as Ras+ and is a cancer-causing mutation. What effect do you think this mutation will have on signaling downstream of Ras+? Why? a)A mutation would turn on the signaling pathway all of the time. b)Even if a route is mutated, it can still be turned on or off. c)Due to a mutation, the signaling pathway would always be off.arrow_forwardIf some cell-surface receptors, including Notch, can rapidly signal to the nucleus by activating latent transcription regulators at the plasma membrane, why do most cell- surface receptors use long, indirect signaling cascades to influence gene transcription in the nucleus?arrow_forward
- The output of RTK pathways is often the activation of MAP Kinase. Explain how MAPK can lead to activation of a specific subset of proteins, leading to distinct effects in different cell types in response to the same growth signal.arrow_forwardCompare and contrast GPCR and RTK signaling. What role does GTP play in each? What role does phosphorylation play? How do these two signaling types compare to steroid signaling with respect to gene activation?arrow_forwardIf you have a protein kinase that is regulated by both small molecule inhibitors as well as by phosphorylation, and is part of a cooperative enzyme complex that works as part of a larger pathway involving kinase and GTPase proteins please explain where on this protein regulation could occur, how different types of inhibition could control the function of the protein as well as the function of the complex, and how the protein could regulate other proteins. (This question was previously answered but it was answered incompletely mentioning an herbicide developed in the 1950's. Apparently, it was a plagiarized excerpt from an NCBI article. This is a repost for a full and complete answer. Thank you so much for your help! :) )arrow_forward
- What is meant by intrinsic GTPase activity? Exchange of GDP for GTP on the a-subunit of the G protein Inhibition of GBCR receptor activity Activation of Adenylyl Cyclades Breakdown of cAMP by phosphodiesterase Spontaneous hydrolysis of GTP on the a-subunit of the G-proteinarrow_forwardWhile investigating the function of a specific growth factor receptor gene from humans, researchers found that two types of proteins are synthesized from this gene. A larger protein containing a membrane spanning domain recognizes growth factors at the cell surface, stimulating a specific downstream signaling pathway. In contrast, a related, smaller protein is secreted from the cell and binds available growth factor circulating in the blood, thus inhibiting the downstream signaling pathway. Speculate on how the cell synthesizes these disparate proteins.arrow_forwardTo move in a specific direction, a migrating cell must use extracellular cues to establish which portion of the cell will act as the front and which will act as the back. Describe how small GTPase proteins appear to be involved in the signaling pathways used by migrating cells to determine direction of movement.arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
