
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The melting point of nonane should be predicted from the given table.
- Greater than that of octane
- Less than that of heptane
- Greater than that of decane
- Less than that of hexane
Concept introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms.
Answer to Problem 6STP
The melting point of nonane is greater than that of octane. Thus, option (A) is correct.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
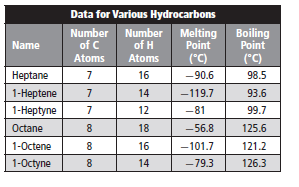
Melting point is defined as a temperature at which a substance changes its state from solid to liquid state. Melting point increases with increase in intermolecular forces or attraction present in the molecule.
Now, intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals forces increases with increase in surface area of electron clouds which are interacting with each other. Thus, a small molecule has less surface of electron cloud whereas a large molecule has greater surface area of electron cloud implies greater Van der Waals forces with molecules.
Therefore, from above facts one can say that the molecule having greater molar mass has more surface area and results in more Van der Waals forces. Thus, more will be the melting point.
Given molecule is nonane.
Molecular formula of nonane is
Molar mass of nonane is 128.2 g/mole.
(A)
Molecular formula of octane is
Molar mass of octane is 114.23 g/mole.
Now, molar mass of octane is less than the molar mass of nonane. Thus, due to larger surface area, Van der Waals forces or attraction is more in nonane in comparison to octane.
Hence, melting point of nonane is more than the octane due to greater Van der Waals forces.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
CHEMISTRY-TEXT
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





