
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether nylon is formed via addition or condensation
Concept introduction:
The monomer units combined together to form
In addition polymerization, two monomer units add together without release of any side product. In condensation polymerization, addition of two monomer units takes place with release of side product.
Explanation of Solution
The given polymer is nylon.
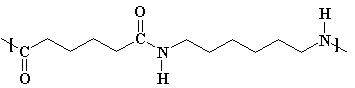
The formation of polymer is represented as follows:
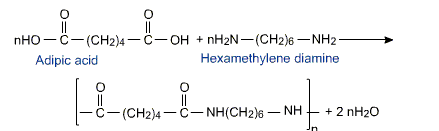
From the above equation, it is formed by two monomers adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine. This results in the removal of water thus, it is a condensation polymerization.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether polyacrylonitrile is formed via addition or condensation polymerization needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The monomer units combined together to form polymer in the polymerization reaction. There are two types: addition and condensation polymerization.
In addition polymerization, two monomer units add together without release of any side product. In condensation polymerization, addition of two monomer units takes place with release of side product.
Explanation of Solution
The given polymer is as follows:
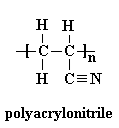
The formation of polymer is represented as follows:

From the above reaction, acrylonitrile is the monomer which undergoes free radical polymerization to form polyacrylonitrile. This is an addition polymerization.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether polyurethane is formed via addition or condensation polymerization needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The monomer units combined together to form polymer in the polymerization reaction. There are two types: addition and condensation polymerization.
In addition polymerization, two monomer units add together without release of any side product. In condensation polymerization, addition of two monomer units takes place with release of side product.
Explanation of Solution
The given polymer is as follows:
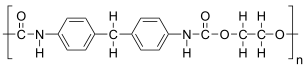
The formation of polymer is represented as follows:
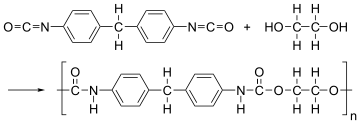
From the above reaction, it is formed by condensation polymerization of polyol (alcohol containing more than 2 hydroxyl groups which are reactive) and diisocyanate in the presence of a catalyst.
This is not a condensation polymerization because no molecule is lost thus, it is an addition polymerization.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether polypropylene is formed via addition or condensation polymerization needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The monomer units combined together to form polymer in the polymerization reaction. There are two types: addition and condensation polymerization.
In addition polymerization, two monomer units add together without release of any side product. In condensation polymerization, addition of two monomer units takes place with release of side product.
Explanation of Solution
The given polymer is as follows:
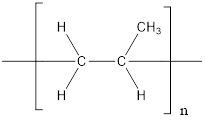
The formation of polypropylene is represented as follows:
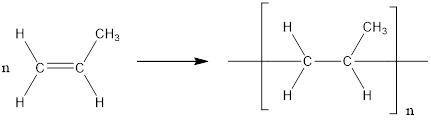
From the above reaction, the above polymer is formed from propylene via addition polymerization.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (5th Edition) (Standalone Book)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
Inorganic Chemistry
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





