
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 49P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
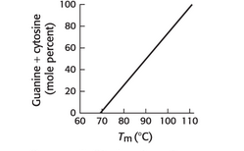
A reasonable explanation for the relation between % of GC base pairs in DNA and the melting temperature needs to be given.
Concept introduction:
The GC base pair i.e. Guanine - Cytosine pair help the DNA to maintain its helical structure which is dependent on the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
May you please help me with this?
A sample of purified DNA was incubated with deoxyribonuclease (DNAse) at 37oC. An
aliquot was removed from the reaction mixture every minute for 5 minutes and
the A260 recorded. The following data were obtained.
Time (min) A260
0 0.60
1 0.64
2 0.67
3 0.70
4 0.72
5 0.73
Describe the action of deoxyribonuclease on DNA and explain the increase in
A260.
Ethanol promotes bonding between Na+ ions from the salt and charged phosphate group of the DNA due to a higher dielectric constant than water.
True or False?
Ethanol (CH3-CH2-OH) is miscible in water because it is
able to form hydrogen bonds with itself and other molecules. However, its structure only allows it to form 1-2 hydrogen bonds. This is one reason why even low concentrations of ethanol in solution are lethal for cells.
Based on this information, explain why we can use high concentrations of ethanol to precipitate DNA out of solution.
Also, describe/predict the effects of increasing concentrations of ethanol in (and around) a cell on macro-molecular interactions (i.e. on weak bonds).
Finally, it is possible to select for yeast that are tolerant to increased concentrations of ethanol. Give an example of a physiological change in yeast cells that might make them resistant to ethanol.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Biochemistry
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1PCh. 4 - Prob. 2PCh. 4 - Prob. 3PCh. 4 - Prob. 4PCh. 4 - Prob. 5PCh. 4 - Prob. 6PCh. 4 - Prob. 7PCh. 4 - Prob. 8PCh. 4 - Prob. 9PCh. 4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 4 - Prob. 11PCh. 4 - Prob. 12PCh. 4 - Prob. 13PCh. 4 - Prob. 14PCh. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - Prob. 16PCh. 4 - Prob. 17PCh. 4 - Prob. 18PCh. 4 - Prob. 19PCh. 4 - Prob. 20PCh. 4 - Prob. 21PCh. 4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4 - Prob. 24PCh. 4 - Prob. 25PCh. 4 - Prob. 26PCh. 4 - Prob. 27PCh. 4 - Prob. 28PCh. 4 - Prob. 29PCh. 4 - Prob. 30PCh. 4 - Prob. 31PCh. 4 - Prob. 32PCh. 4 - Prob. 33PCh. 4 - Prob. 34PCh. 4 - Prob. 35PCh. 4 - Prob. 36PCh. 4 - Prob. 37PCh. 4 - Prob. 38PCh. 4 - Prob. 39PCh. 4 - Prob. 40PCh. 4 - Prob. 41PCh. 4 - Prob. 42PCh. 4 - Prob. 43PCh. 4 - Prob. 44PCh. 4 - Prob. 45PCh. 4 - Prob. 46PCh. 4 - Prob. 47PCh. 4 - Prob. 48PCh. 4 - Prob. 49PCh. 4 - Prob. 50PCh. 4 - Prob. 51PCh. 4 - Prob. 52P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Helicase Unwinding of the E. coli Chromosome Hexameric helicases, such as DnaB, the MCM proteins, and papilloma virus El helicase (illustrated in Figures 16.22 to 16.25), unwind DNA by passing one strand of the DNA duplex through the central pore, using a mechanism based on ATP-dependent binding interactions with the bases of that strand. The genome of E. coli K12 consists of 4,686,137 nucleotides. Assuming that DnaB functions like papilloma virus El helicase, from the information given in Chapter 16 on ATP-coupled DNA unwinding, calculate how many molecules of ATP would be needed to completely unwind the E. coli K 12 chromosome.arrow_forwardSemiconservative or Conservative DNA Replication If 15N-Iabeled E. coli DNA has a density of 1.724 g/mL, 14N-labeled DNA has a density of 1.710 g/mL, and E. coli cells grown for many generations on 14NH4+as a nitrogen source are transferred to media containing 15NH4+as the sole N-source, (a) What will be the density of the DNA after one generation, assuming replication is semiconservative? (b) Suppose replication took place by a conservative mechanism in which the parental strands remained together and the two progeny strands were paired. Design an experiment that could distinguish between semiconservative and conservative modes of replication.arrow_forwardNumber of Okazaki Fragments in E. coli and Human DNA Replication Approximately how many Okazaki fragments are synthesized in the course of replicating an E. coli chromosome? How many in replicating an “average� human chromosome?arrow_forward
- Suggest a reasonable strategy for the specific phosphorylation of the5’ –OH group of a nucleoside.arrow_forwardBoth DNA polymerase (any DNA polymerase) and ligase catalyze the formation of a bond between nucleotides, but these two enzymes do NOT catalyze the same reaction. Briefly describe the differencesbetween the reaction catalyzed by the polymerase activity of DNA polymerase and the one catalyzed by ligase.arrow_forwardP2. Calculate the frictional coefficient of a molecule of DNA of 20 base pairs in water at 20C; assume that the hydrodynamic behavior of the DNA itself can be approximated to be rod-like; the viscosity of the solvent is 0.01 g cm-1 s -1arrow_forward
- Staphylococcus nuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of DNA.The reaction is catalyzed by Ca2+, Glu 43, and Arg 87. Explain how the metal catalyst facilitates this reaction. Recall that the nucleotides in DNA havephosphodiester linkages.arrow_forward2) When DNA is placed in distilled water, which is pH 7.0, it denatures (i.e., the two strands separate). The pH inside a cell is generally 7.2-7.5, depending on the organism, but DNA is generally double-stranded under physiological conditions. Briefly explain, in your own words, why DNA denatures when placed in distilled water but not when it is inside a cell. [Reminder: the pKa for the phosphate groups in the sugar-phosphate backbone of a strand of DNA is 2.14]arrow_forwardWhich conformation of DNA – (i) totally double helix, (ii) minimally unwound or (iii) largely unwound – would have the highest relative absorbance at 260 nm. Would a molecule of DNA having a higher content of guanine and cytosine than of adenine and thymine have a higher or lower melting temperature (Tm) than one with the reverse composition?arrow_forward
- just choose dont explain The alternating sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA is hydrophobic Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardEnediynes are natural products with potent antitumor properties because they are able to cleave DNA (page 288). Their cytotoxic properties are due tothe enediyne undergoing a cyclization to form a highly reactive diradical intermediate. The intermediate abstracts hydrogen atoms from the backbone of DNA, which triggers its damage. Draw the structure of the diradical intermediate.arrow_forwardNot just generic "degradation" or even shorter DNA fragments, what specific structure change in double-stranded DNA does the hyperchromicity effect show?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Macromolecules | Classes and Functions; Author: 2 Minute Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5hhrDFo8Vk;License: Standard youtube license