
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of anisaldehyde with
Concept Introduction:
Addition of H2gas to a multiple bond is known as hydrogenation. In the presence of palladium metal as the catalyst H2 molecules react with
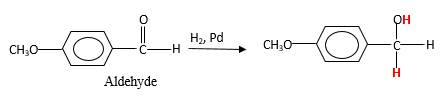
Answer to Problem 76P
Explanation of Solution
When an aldehyde reacts with H2 gas in the presence of palladium metalresulting product is an alcohol of the initial aldehyde molecule. Palladium metal act as a catalyst to the reaction that provides a surface to bind both the H2 and carbonyl compound which reduce the activation energy of the reaction.
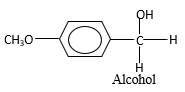
Hydrogen atoms in the alcohol molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added H during the hydrogenation reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
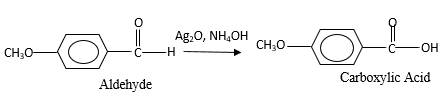
The products should be identified by the reaction of anisaldehyde with
Concept Introduction:
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. The hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C in an aldehyde will oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as
Oxygen atom in the carboxylic acid molecule shown below, which is indicated in red color is the added O during the oxygenation reaction.
Answer to Problem 76P
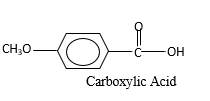
Explanation of Solution
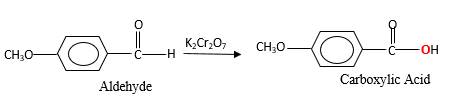
When an aldehyde reacts with
Oxygen atom in the carboxylic acid molecule shown below, which is indicated in red color is the added O during the oxygenation reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of anisaldehyde with
Concept Introduction:
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. The hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C in an aldehyde will oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as (
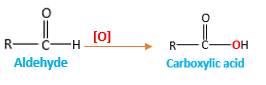
Answer to Problem 76P
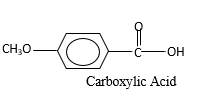
Explanation of Solution
When an aldehyde reacts with
Aldehyde's
(d)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of anisaldehyde with
Concept Introduction:
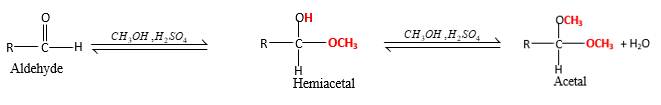
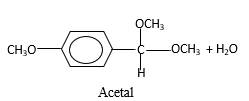
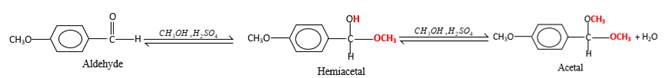
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, aldehydes undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps.
Hydrogen atom and CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
Answer to Problem 76P
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, aldehydes undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps. In the first step aldehydes form hemiacetals and during the second step it converts to an acetal molecule of the respective aldehyde molecule.
Addition of one molecule of alcohol in to an aldehyde forms a hemiacetal, one bond of the
(e)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of anisaldehyde with
Concept Introduction:
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, aldehydes undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps.
Hydrogen atom and CH2CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
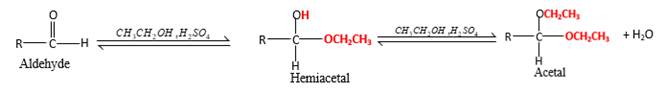
Answer to Problem 76P
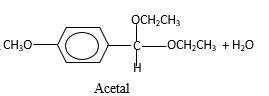
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, aldehydes undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps. In the first step aldehydes form hemiacetals and during the second step it converts to an acetal molecule of the respective aldehyde molecule.
Addition of one molecule of alcohol in to an aldehyde forms a hemiacetal, one bond of the
Hydrogen atom and CH2CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
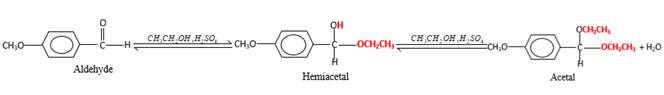
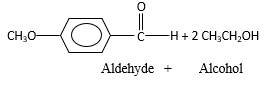
(f)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of
Concept Introduction:
In the presence of waterandacid, acetals undergo hydrolysis reaction and produce aldehydes.
OR' groups in the acetal molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the molecules which becomes alcohol molecules during the hydrolysis.
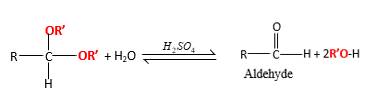
Answer to Problem 76P
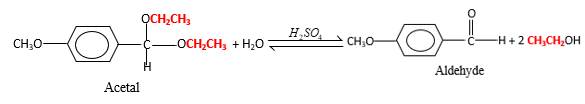
Explanation of Solution
Acetals are stable molecules, but their bonds can cleave by a reaction with water and produce aldehydes.
In the acetal molecule, two bonds of the
CH2CH3 groups in the acetal molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the molecules which becomes alcohol molecules during the hydrolysis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Thioglycolic acid, HSCH2CO2H, a substance used in depilatory agents (hair removers) has pKa = 3.42. What is the percent dissociation of thioglycolic acid in a buffer solution at pH = 3.0?arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when D-altrose is treated with each reagent. a. (CH3)2CHOH, HCl b. NaBH4, CH3OH c. Br2, H2O d. HNO3, H2O e. [1] NH2OH; [2] (CH3CO)2O, NaOCOCH3; [3] NaOCH3 f. [1] NaCN, HCl; [2] H2, Pd-BaSO4; [3] H3O+ g. CH3I, Ag2O h. C6H5CH2NH2, mild H+arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when (CH3)2CHOH is treated with each reagent (a, b and c)arrow_forward
- Draw the products formed when ethylene oxide is treated with each reagent. a. HBr b. H2O(H2SO4) c. [1] CH3CH2O; [2] H2O d. [1] HC ≡ C−; [2] H2O e. [1] −OH; [2] H2O f. [1] CH3S−; [2] H2Oarrow_forwardOne reagent used ? Q2arrow_forwardDraw the missing starting material. Reagent 1 is benzene and AlCl3. Reagent B is Zn(Hg) and HCl.arrow_forward
- what reagents are needed?arrow_forward1. what priority functional group of ff organic compound? a. carboxyl b. hydroxide c. hydroxyl d. carbonyl 2. what group does the ff organic compound belong? a. azo b. diazo c. aromatic d. organosulfur 3. what group does the ff organic compound belong? a. azo b. amines c. diazo d. nitrilesarrow_forwardAmino acids such as glycine are the building blocks of large molecule.called proteins that give structure to muscle, tendon, hair, and nails.a.Explain why glycine does not actually exist in the form with all atoms uncharged, but actually exists as a salt called a zwitterion. b.What product is formed when glycine is treated with concentrated HCl? c. What product is formed when glycine is treated with NaOH?arrow_forward
