
(a)
Interpretation:
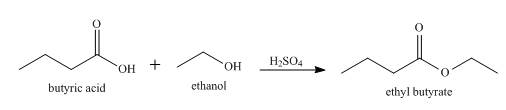
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Esterification occurs when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. Esters end with a suffix,
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
When butyric acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of

Figure 1
When butyric acid reacts with ethanol in presence of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with aqueous
Concept introduction:
An acid-base reaction occurs through a transfer of proton from an acid to a base. The base gets protonated and the acid gets deprotonated. The reaction results in the formation of a conjugate acid and a conjugate base as the products. The type of products formed affects the direction of reaction at equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with aqueous
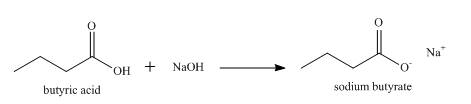
Explanation of Solution
When a carboxylic acid reacts with a base, the hydrogen atom is abstracted by the base and a salt of carboxylic acid is formed.
So, when butyric acid reacts with aqueous

Figure 2
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with aqueous
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with
Concept introduction:
The substances which on addition removes oxygen atom or hydrogen atom from the other substance, that is, reduces the other substances are known as reducing agents. Reducing agents themselves get oxidized. Carboxylic acid is reduced when reacts with reducing agent,
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with
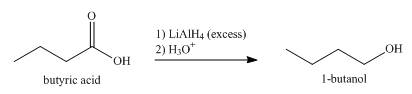
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acid is reduced when reacts with reducing agent,
When butyric acid reacts with excess of

Figure 3
When butyric acid reacts with excess of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butyric acid is heated is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids such as
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
When butyric acid is heated, no product is formed.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of butyric acid does not have any electron-withdrawing group like
Butyric acid on heating gives no reaction.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with
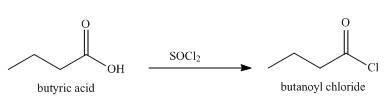
Explanation of Solution
When butyric acid reacts with

Figure 4
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with diazomethane in ether is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Esterification occurs when carboxylic acid reacts with diazomethane in ether. Esters end with a suffix,
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with diazomethane in ether is shown below.
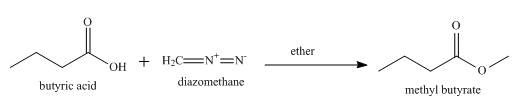
Explanation of Solution
Esterification occurs when butyric acid reacts with diazomethane in ether and methyl butyrate is formed as a product along with the release of nitrogen gas. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 5
The product formed when butyric acid reacts with diazomethane in ether is methyl butyrate.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept introduction:
Acetal is formed when an alcohol in excess reacts with an aldehyde or ketone in acidic medium. The
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when
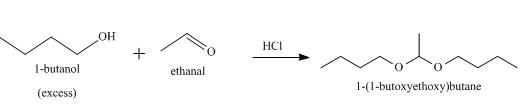
Explanation of Solution
When an alcohol reacts with an aldehyde in presence of an acid catalyst, a hemiacetal is formed as an intermediate which further reacts to produce acetal with the release of water. The acidic catalyst is used because the alcohol is a weak nucleophile. So on addition of an acid, the oxygen of aldehyde gets protonated and a carbocation is formed. The alcohol easily attacks the carbocation to form the germinal diether derivative of aldehyde, that is, an acetal. When

Figure 6
When
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed when butanoyl chloride reacts with benzene in
Concept introduction:
Friedel crafts acylation reaction is a reaction in which an
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when butanoyl chloride reacts with benzene in
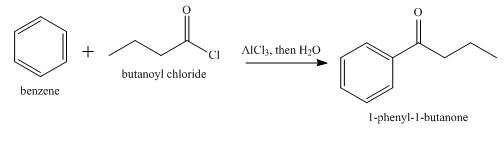
Explanation of Solution
Benzene undergoes Friedel Crafts acylation reaction on reaction with butanoyl chloride in presence of

Figure 7
The product formed when butanoyl chloride reacts with benzene in
(i)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept introduction:
Wolff Kishner Reduction is a reaction in which aldehydes and ketones are converted into
Answer to Problem 20.27AP
The product formed when
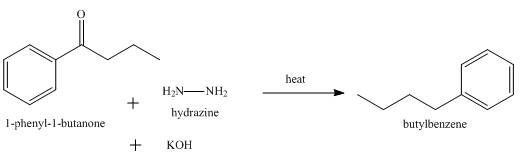
Explanation of Solution
Wolff Kishner reduction takes place when

Figure 8
The product formed when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry 2.1. Why are so many routes available for the creation of acetic acid? 2.2. Benzene is a high-commodity aromatic material with many industrial applications but is produced in relatively small amounts through petroleum fractionation. Explain how Toluene can be converted to benzene, please be specific in terms of reagents and conditions.arrow_forwardprovide the reagents necessary to complete the following information.arrow_forwardGive the expected organic product when phenylacetic acid, PhCH2COOH, is treated with reagent Q.)LiAlH4 followed by H2Oarrow_forward
- Write the equilibrium-constant expressions and obtainnumerical values for each constant in. (a) the basic dissociation of aniline, C6H5NH2. (b) the acidic dissociation of hypochlorous acid,HClO. (c) the acidic dissociation of methyl ammoniumhydrochloride, CH3NH3Cl. (d) the basic dissociation of NaNO2. (e) the dissociation of H3AsO3to H3O+and AsO33-. (f) the reaction of C2O42-with H2O to give H2C2O4and OH-. show solutionarrow_forwardSeveral sulfonylureas, a class of compounds containing RSO2NHCONHR, are useful drugs as orally active replacements for injected insulin in patients with adult-onset diabetes. These drugs decrease blood glucose concentrations by stimulating b cells of the pancreas to release insulin and by increasing the sensitivity of insulin receptors in peripheral tissues to insulin stimulation. Tolbutamide is synthesized by the reaction of the sodium salt of p-toluenesulfonamide and ethyl N-butylcarbamate . Propose a mechanism for this step.arrow_forwardQ2) Write a reaction for the following, with explanation. part 1) Dimethyl ketone with Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) part2) Preparation of M. nitro chlorobenzene from benzene, using nitric acid Sulfuric acid, Chlorine, AICI, and any reagent you need. part3) Solvation of ethylene epoxide in acidic mediumarrow_forward
- Give the expected organic product when phenylacetic acid, PhCH2COOH, is treated with reagent Q.)NaOH, H2Oarrow_forwardWhat is the structural requirement for a substance to react with ammoniacal AgNO3? Why would acetylene react with Tollen's reagent but not cyclohexane or cyclohexene?arrow_forwardQuinolines, heterocyclic compounds that contain a pyridine ring fused to a benzene ring, are commonly synthesized by a method known as the Skraup synthesis, in which aniline reacts with glycerol under acidic conditions. Nitrobenzene is added to the reaction mixture to serve as an oxidizing agent. The first step in the synthesis is the dehydration of glycerol to propenal. a. What product would be obtained if para-ethylaniline were used instead of aniline? b. What product would be obtained if 3-hexen-2-one were used instead of glycerol? c. What starting materials are needed for the synthesis of 2,7-diethyl-3-methylquinoline?arrow_forward
- A synthetic organic molecule, G, which contains both aldehyde and ether functional groups, is subjected to a series of reactions in a multi-step synthesis pathway. In the first step, G undergoes a Wittig reaction, leading to the formation of an alkene, H. Subsequently, H is treated with an ozone (O3) reagent followed by a reducing agent in an ozonolysis reaction, resulting in the formation of two different products, I and J. Considering the functional groups present in G and the nature of the reactions involved, what are the most probable structures or functional groups present in products I and J? A. I contains a carboxylic acid group, and J contains an aldehyde group. B. I contains a ketone group, and J contains an alcohol group. C. I and J both contain aldehyde groups. D. I contains an ester group, and J contains a ketone group. Don't use chat gpt.arrow_forwardWhen methanitrobenzoic acid is reacted with bromomethane in the presence of Lewis acids, which of the following is the product?arrow_forwardWrite the formula of reagents used in the following reactions:(i) Bromination of phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol(ii) Hydroboration of propene and then oxidation to propanol.(b) Arrange the following compound groups in the increasing order of their property indicated:(i) p-nitrophenol, ethanol, phenol (acidic character)(ii) Propanol, Propane, Propanal (boiling point)arrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


