
(a)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
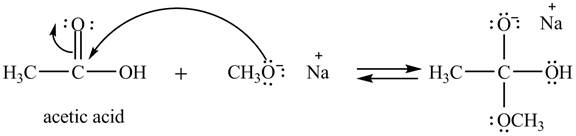
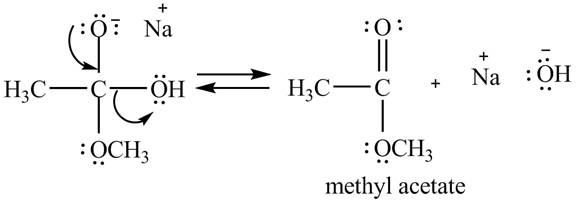
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of sodium methoxide with a carboxylic acid produces an ester. The steps for the formation of the product of the reaction between
In the first step, the electron pairs of oxygen present in methoxide ion attacks the acyl carbon atom of acetic acid and bonding pair of electrons present in the pi bond of acyl group shifts towards oxygen atom simultaneously. Due this an intermediate is formed as shown below.
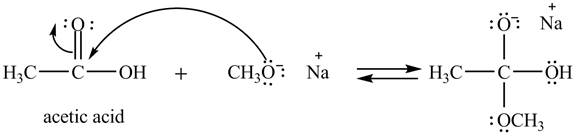
Figure 1
In the second step, the regeneration of the acyl group takes place by the movement of electron pair of negative charged oxygen atom and also the removal of hydroxide ion takes place from the intermediate simultaneously. Hydroxide ion gets removed by grabbing the electron pair of

Figure 2
Therefore, methyl acetate is desired product formed by the reaction of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of ![]() of acetic acid are shown below.
of acetic acid are shown below.
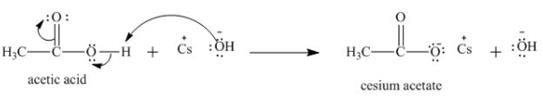
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of a base like
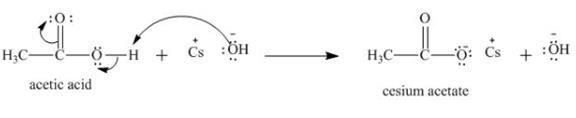
Figure 3
Therefore, cesium acetate is desired product formed by the reaction of ![]() of
of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of ![]() of acetic acid and the corresponding curved-arrow notation are to be stated.
of acetic acid and the corresponding curved-arrow notation are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
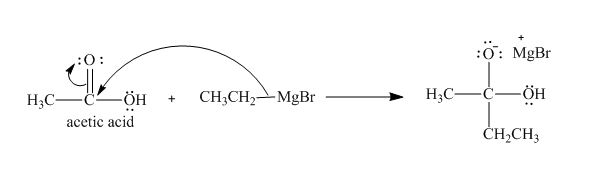
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of Grignard reagent with a carboxylic acid results into a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The steps for the formation of the product of the reaction between
In the first step, the bonding electron pairs of

Figure 4
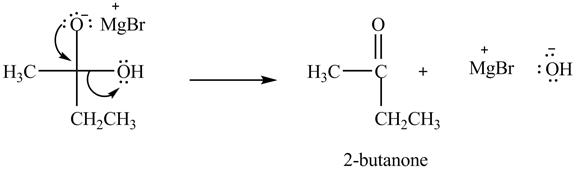
In the second step, the regeneration of the acyl group takes place by the movement of electron pair of negative charged oxygen atom and also the removal of hydroxide ion takes place from the intermediate simultaneously. Hydroxide ion gets removed by grabbing the electron pair of

Figure 5
Therefore, ![]() of
of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
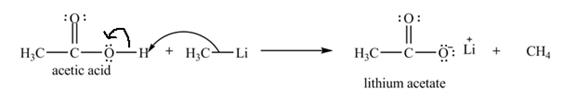
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of a base like

Figure 6
Therefore, lithium acetate is desired product formed by the reaction of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(e)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
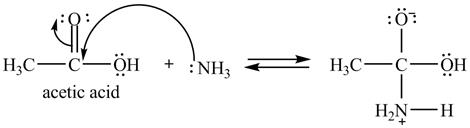
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of ammonia with a carboxylic acid results into a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The steps for the formation of the product of the reaction between
In the first step, the lone of pair of electrons of
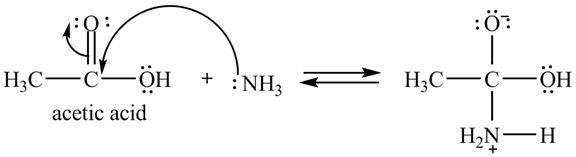
Figure 7
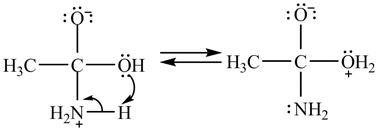
In the second step, electron pairs of oxygen in
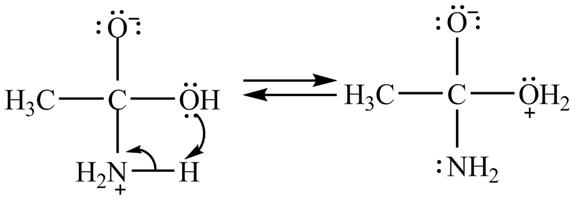
Figure 8
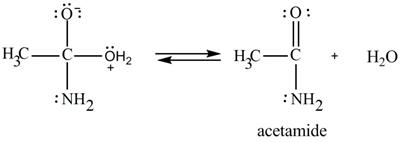
In the third step, the regeneration of the acyl group takes place by the movement of electron pair of negative charged oxygen atom and also the removal of hydroxide ion takes place from the intermediate simultaneously. Hydroxide ion gets removed by grabbing the electron pair of
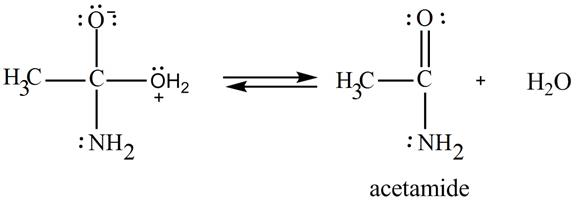
Figure 9
Therefore,
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(f)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
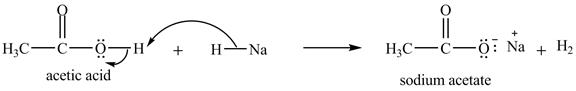
Explanation of Solution
The treatment of a base like
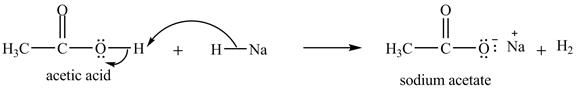
Figure 10
Therefore, sodium acetate is desired product formed by the reaction of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
(g)
Interpretation:
The product which is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The curved-arrow notation is used to show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The curved arrow has two barbs (head and tail) which represent the direction of electron flow.
Answer to Problem 20.31AP
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
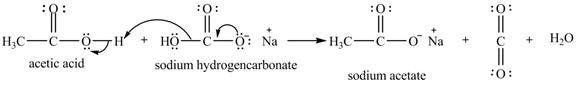
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
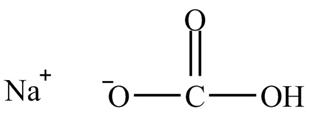
Figure 11
The given compound is sodium hydrogencarbonate. The treatment of a base like sodium hydrogencarbonate with acetic acid produces a salt known as sodium acetate. In the first step of the reaction between
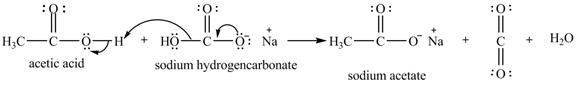
Figure 12
Therefore, sodium acetate is desired product formed by the reaction of
The curved arrow notation and product for the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- When the 2.5M NaOH (15mL) solution is added to the solution of 50:50 mixture of benzophenone and benzocaine acid (2.001g) , in diethyl ether (30 mL), a reaction takes place between NaOH and one of the components in the mixture. Draw a scheme that shows that reaction. Include electron-push arrowsarrow_forwardDetermine the direction of equilibrium when acetylene (HC≡CH) reacts with−NH2 in a proton transfer reaction ?arrow_forwardwhat happens when I add 3 H2O + C6H8O7 → Please explain if there is more than one reaction for disotiation.arrow_forward
- Predict the products of the reactants below? (NH4)(NO3) + Al(OH)3----> which one below is the correct awnser (NH4)(NO3) + Al(OH)3 (NH4)(OH) + Al(NO3) (NH4)(OH) + Al(NO3)3 (NH4)(OH)2+ Al(NO3)3arrow_forwardDraw an energy diagram for a reaction with keq = 1. What is the value of ∆G° in this reaction?arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 0.1 M solution of methylamine hydrochloride (CH3NH3Cl), if pKb of CH3NH2 = 4?arrow_forward
- For each case below determine whether the products or reactant are favored A reaction of K eq=10 A reaction of K eq = 0.01 A reaction of negative delta Garrow_forwardwhich is the major product of the reaction I II III IV Varrow_forwardComplete the balanced dissociation equation for the compound below in aqueous solution. If the compound does not dissociate, write NR after the reaction arrow. Cs2CO3(s) = Complete the balanced dissociation equation for the compound below in aqueous solution. If the compound does not dissociate, write NR after the reaction arrow. Mg(OH)2(s) =arrow_forward
- Calculate the Ka's for the following acids: (a) Citric acid, pKa = 3.14 (b) Tartaric acid, pKa = 2.98arrow_forwardThe normal pH range for blood plasma is 7.35–7.45. Under these conditions, would you expect the carboxyl group of lactic acid (pKa 3.08) to exist primarily as a carboxyl group or as a carboxylic anion? Explain.arrow_forwardc) Describe the relative position of the equilibrium if Keq = 1.76 x 10-5arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

