
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of 2-methylpentanal needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(a)
Answer to Problem 67A
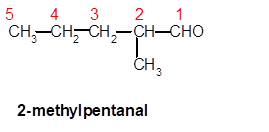
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
In 2-methylpentanal, pent- is root word so there must be 5 C atoms in chain with one methyl group at C-2 and one −CHO group at C-1.
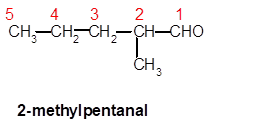
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(b)
Answer to Problem 67A
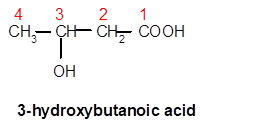
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
In 3-hydroxybutanoic acid, but- is root word so there must be 4 C atoms in chain with one hydroxy group at C-3 and one −COOH group at C-1.
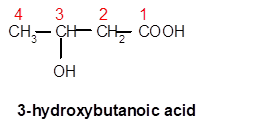
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of 2-aminopropanal needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(c)
Answer to Problem 67A
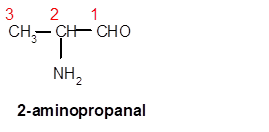
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
In 2-aminopropanal, prop- is root word so there must be 3 C atoms in chain with one amino group at C-2 and one −CHO group at C-1.
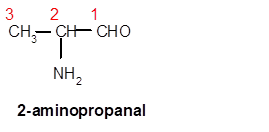
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of 2,4-hexanedione needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(d)
Answer to Problem 67A
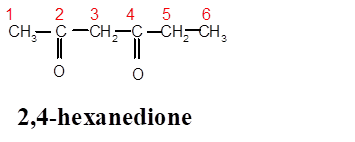
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
In 2,4-hexanedione, hex- is root word so there must be 6 C atoms in chain with two
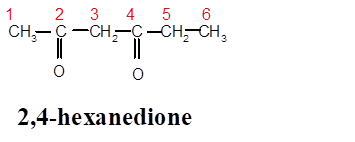
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of 3-methylbenzaldehyde needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(e)
Answer to Problem 67A
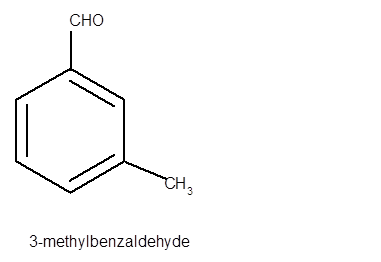
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
In 3-methylbenzaldehyde, benzene ring should be root word with one
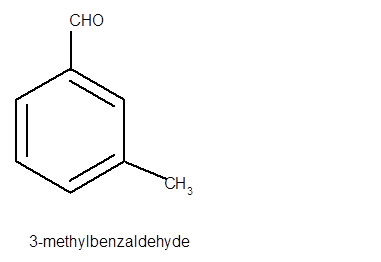
Chapter 20 Solutions
World of Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





