
Concept explainers
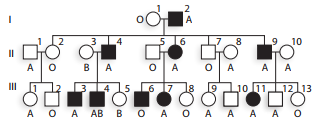
a. Is
b. Does this family give evidence of genetic linkage between
c. Using N and n to represent alleles at the
d. Explain why
e. Explain why
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- Does the phenotype indicated by the red circles and squares in this pedigree show an inheritance pattern that is autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked?arrow_forwardFamilial retinoblastoma, a rare autosomal dominant defect, arose in a large family that had no prior history of the disease. Consider the following pedigree (the darkly colored symbols represent affected individuals): a. Circle the individual(s) in which the mutation most likely occurred. b. Is the person who is the source of the mutation affected by retinoblastoma? Justify your answer. c. Assuming that the mutant allele is fully penetrant, what is the chance that an affected individual will have an affected child?arrow_forwardThe following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of Nance–Horan syndrome, a rare genetic condition in which affected people have cataracts and abnormally shaped teeth.arrow_forward
- The following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of ringed hair, a condition in which each hair is differentiated into light and dark zones. What mode or modes of inheritance are possible for the ringed-hair trait in this family?arrow_forwardCould the pedigree in Figure 2-31 be explained as an autosomal dominant disorder? Explain.arrow_forwardThe following pedigree describes the inheritance of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, an x-linked recessive disease. Affected individuals are shaded. what is the probability, that the indicated child (IV.1) will be affected by Lesch-Nyhan syndrome? show solutionarrow_forward
- Ectrodactyly is a rare condition in which the fingers are absent, and the hand is split. It is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. What do the double horizontal lines mean between III-1 and III-4? Is the pedigree below consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance?arrow_forwardChands syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by very curly hair, underdeveloped nails, and abnormally shaped eyelids. In the pedigree below: Which individuals must be carriers (heterozygotes)? ----- arrow_forwardThe pedigree below represents the inheritance of a rare genetic disorder (members joining the pedigree are not carriers). Consider the following pedigree and answer questions (i) to (vii) below. The allele descriptors are B/b. What is the mode of inheritance in this pedigree ? Y-linked inheritance X-linked recessive inheritance X-linked dominant inheritance Autosomal recessive inheritance Autosomal dominant inheritance What is the genotype of individual III-2 ? a) XbXb b) XBXB c) XBXb d) Bb e) bb What is the genotype of individual IV-3 ? a) XbXb b) XBXB c) XBXb d) Bb e) bb Individual IV-4 and an unaffected woman is planning a family. What is the probability that their first child will be phenotypically normal ? a) chance that the first child will be phenotypically normal. b) chance that the first child will be phenotypically normal. c) chance that the first female child will be phenotypically normal; all male children will be phenotypically normal. d) chance that the…arrow_forward
- Is this pedigree dominant or recessive. Which best defines this pedigree Autosomal or sex-linked?arrow_forwardTake the example of B-thalassemia, an autosomal recessive genetic disease that particularly affects people from around the Mediterranean. This disease is associated with an anomaly of hemoglobin, a protein essential for the transport of oxygen, which is composed of four chains: two alpha (a) and two beta (B). In case of B-thalassemia, the ẞ chains are produced in insufficient or no quantity in an individual homozygous recessive resulting in insufficient production of overall hemoglobin leading to anemia and other physiological challenges. The gene that controls the synthesis of the ẞ chains is located on chromosome 11. Here is part of the coding portion of this gene (which controls a total of 146 amino acids and of which you only see the portion 36 to 41) and one of the targeted mutations: 1. Give the sequence of amino acids from the template and mutated strands. 2. What type of point mutation is it? 3. Using the principles of the theory of evolution, explain briefly and generally why…arrow_forwardBelow is a pedigree chart for a family that has a history of Alkaptonuria. Individuals infected with this condition can have darkened skin, brown urine, and can suffer from joint damage and other complications. Given this pedigree answer the following questions. Given the data in the pedigree chart is this genetic condition autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive? What are the genotypes for #1, #2, and #3? If either of the 4th generation "aa" females were to mate with a homozygous dominant male would any of their offspring illustrate the phenotype? Why or why not?arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning


