
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Whether the pair of two molecules representconstitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
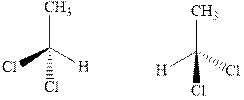
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(b)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
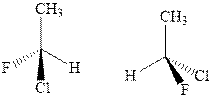
Concept introductionIn order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(c)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
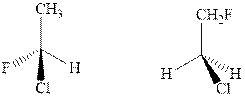
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(e)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(f)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
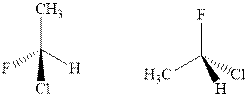
Concept introduction:The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(g)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
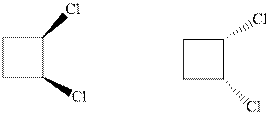
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(h)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(i)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(j)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
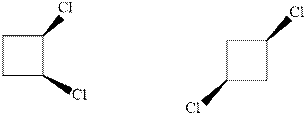
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(k)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
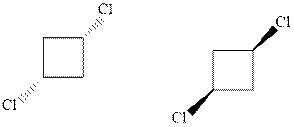
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(l)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
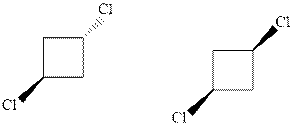
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(m)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
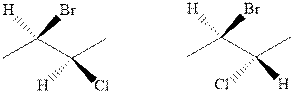
Concept introduction:The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(n)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
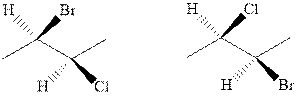
Concept introduction: The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(o)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
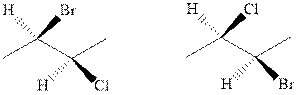
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(p)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
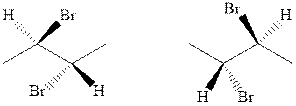
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- For each pair, indicate whether they are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereoisomers, or identical molecules. A BDEFarrow_forwardFor each pair of structures shown, indicate hether the two species are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers of one another, or identical moleculesarrow_forwardFor each of the following pairs of molecules, classify them as either: enantiomers, diastereomers, identical compounds, or constitutional isomers.arrow_forward
- what is the relationship between these compounds, constitutional isomer, enantiomer, diastereomer, same compound?arrow_forwardWhat is the relationship of the following molecule? Are they identical, constituional isomers, enantiomers, or diastereomers?arrow_forwardDetermine the following pairs of structures as: Enantiomers, Diastereomers or neither. If its an enantiomer, indicate the D enantiomer and the L enantiomer.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
