
(a)
Interpretation:Mechanism for the reaction of hydrogen bromide with alkene indicated should be written.
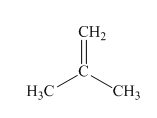
Concept introduction:
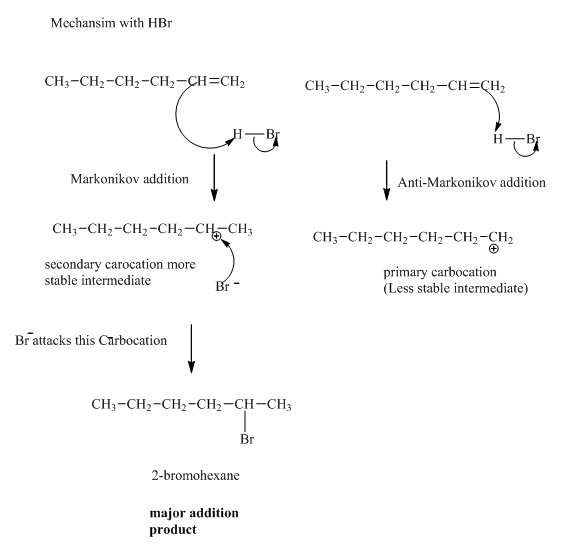
(b)
Interpretation:Mechanism for the reaction of hydrogen bromide with alkene indicated should be written.
Concept introduction:Alkenes are considered electron rich and undergo addition reaction in presence of electrophilic halo acids. The product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
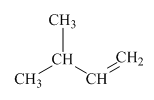
(c)
Interpretation:Mechanism for the reaction of hydrogen bromide with alkene indicated should be written.
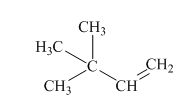
Concept introduction:In electrophilic addition reaction the product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- 1-pentanol (NaBr/H2SO4) --> 1-bromopentane Propose plausible side-products (also called by-products) and write complete curved arrow mechanism for how they might be formed in the reaction.arrow_forwardDraw/outline a reasonable and detailed mechanism for the dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid. Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons and draw the structures of all intermediates and byproducts formed in the reaction. Predict and rationalize the expected product distribution based on thermodynamic aspectsarrow_forwardI am working on a practice assignment for my organic II course and am having difficulty with a question that asks to identify the reaction sequence used to synthesize isopropylcyclopentane. I would really appreciate the help!arrow_forward
- Question: How do quantum mechanical effects influence the stability and reactivity of molecules with non-classical carbocations, such as the 2-norbornyl cation, and how does this impact the reaction mechanisms and outcomes?arrow_forwardDerive 2,4,4-trimethyl-2-pentenal using 2,2-dimethyl propane and other necessary reagents. write, showing the reaction mechanism.arrow_forward3) Outline an acceptable step by step mechanism for the Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of ortho-fluoronitrobenzene with methylamine. Do not forget to include the formal charges of all non-hydrogen atoms that do not have a neutral charge.arrow_forward
- i need help writing all of the detailed methods: in Preparation of Cyclohexanone by Hypochlorite Oxidationarrow_forwardBromine is known to abstract a secondary hydrogen 97 times as rapidly as a primary hydrogen. Predict the product ratio (or percent yield of each product) for the monobromination of n-butane.arrow_forwardMaking use of the corresponding mechanisms and additional comments, justify the following observations A) Mechanism of Formation of the super-electrophile B) COMPLETE mechanism meta position C) COMPLETE mechanism para position D) Explanation of the resultarrow_forward
- Suggest a synthesis for the molecule below starting from benzene, alcohols of four carbons or fewer and any inorganic reagents for questions D-H please provide the full names for the compounds belowarrow_forwardPlease show the electron-flow mechanism of the general synthesis of Sulfonamides,this involves predicting major and by-products using electronic and structural effects. The arrow push mechanism must be shown.arrow_forwardSynthesize from benzene. (Hint: All of these require diazonium ions.)(a) 3-ethylbenzoic acidarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





