
Interpretation:
The products that would be formed on salicin reacting with dilute aqueous HCl is to be determined and the mechanism of reaction for the this reaction is to be outlined.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron-rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a functional group is substituted by any other functional group is called substitution reaction.
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 A carbohydrate is a
舧 Salicin is a naturally occurring glycoside and is originally found in the bark of willow trees. It is an effective analgesic for relieving pain. Its structure is given below:
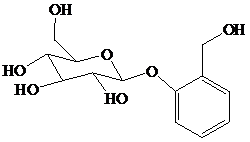
舧 Glycosides are carbohydrate acetals and can be simple or complex. These molecules are stable in basic solutions, but produce sugar and alcohol in acidic solutions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Give only typing answer with explanation and conclusion Which of the following compounds cannot be prepared via acetoacetic ester synthesis.arrow_forwardtert-Butoxycarbonyl azide was developed as a reagent for peptide synthesis at OWL's home institution, the University of Massachusetts, by Prof. L.A. Carpino. It is prepared by treating tert-butoxycarbonyl chloride with sodium azide. Propose a structure for the initially-formed intermediate in this reaction.arrow_forwardWolff-Kishner reduction of compound W gave compound A. Treatment of A with m-chloroperbenzoic acid gave B which on reduction with LiAH4 gave C. Oxidation of compound C with chromic acid gave D (C9H14O). Suggest the structures for A, B, C, and D.arrow_forward
- Explain the products that would be formed when cholesterol is reacted with bromine in an organic solvent. Outline a mechanism for the reaction that takes place.arrow_forward3. Obtain acetophenone and acetaldehyde by reaction of glycols with periodic acid. Justify your answer with the reaction mechanism.arrow_forwardShow how Fischer esterification might be used to form the following esters. In each case,suggest a method for driving the reaction to completion.(a) methyl salicylatearrow_forward
- Compound A has the molecular formula C14H25Br and was obtained by reaction of sodium acetylide (HC≡CNa) )with 1,12-dibromododecane. On treatment of compound A with sodium amide, it was converted to compound B (C14H24). Ozonolysis of compound B gave the diacid HO2C(CH2)12CO2H. Catalytic hydrogenation of compound B over Lindlar palladium gave compound C (C14H26), while hydrogenation over platinum gave compound D (C14H28). Sodium-ammonia reduction of compound B gave compound E (C14H26). Both C and E yielded O═CH(CH2)12CH═O on ozonolysis. Assign structures to compound A through E so as to be consistent with the observed transformations.arrow_forwardOutline the theoretically possible stereochemical outcomes of reduction of benzil. Describe isomers of hydrobenzoin and stereochemical relationships between them.arrow_forwardProvide in detail, the aspirin synthesis mechanism.arrow_forward
- Compound A was oxidized with periodic acid to give B, which after acid hydrolysis gave C. Bromine oxidation of C gave D. Suggest structural formulas, including stereochemistry, for compounds B, C, and D.arrow_forwardIn the preparation of p-Nitroaniline, there are three synthetic steps in this reaction, the first is acetylation of the amine, second is nitrates and the third is hydrolysis of the amide. Why must acetylation be done first if at all? Use chemical structures to illustrate your point.arrow_forwardGive a suitable chemical reaction to distinguish between a primary and a secondary amine. Suggest one way of Increasing the basicity of an amine and give a specific example of its application.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

