
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, water is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
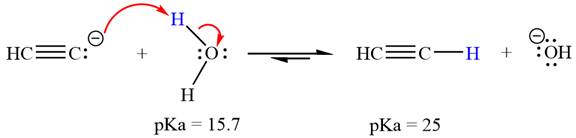
Water,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamide is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
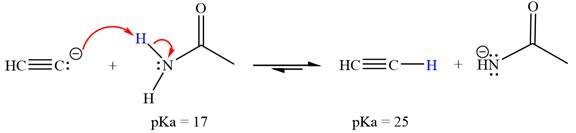
Ethanamide,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
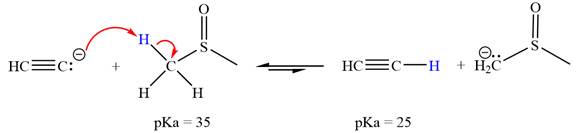
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
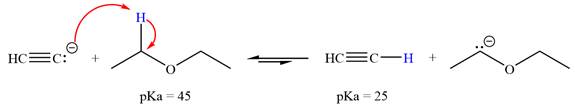
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- What is the percent dissociation of 0.150 M triethylamine? (The Kb value for triethylamine is 5.25 × 10-4.) a. 5.92 %b. 5.75 %c. 39.4 %d. 5.75 x 10-30 %arrow_forward2c)Outline a method based on extraction techniques for the separation of a mixture of compound B from problem I., and compound A from problem II.arrow_forwardNMR of profuct is C5H12O2. Solve for the starting material or product and then fill in the missing componenet to give overall reaction. Use one of this reactions I) CH3OH/H2SO4 2) 1. BH3. 2. H2O2, OH,H20 3) 1. OSO4. 2. NaHSO3 4) H3O+ 5)1. Hg(OAc)2, CH3OH. 2. NaBH4 6) Br2 in CCL4 7) Br2 in CH3OH 8)Br2 in CH3OH 9) Cl2 in H2O Show reaction mechanismarrow_forward
- If i cannot use ammonia water, what can i use as a substitute to make my acid supernatant to be an alkaline? After being macerated with 95% ethanol and dissolved in 5% acetic acid, I got an acid supernatant and I was supposed to use ammonia water along with dichloromethane but the ammonia water was disregarded due to specific reasons. What can I replace my ammonia water with to make my acid supernatant an alkaline?arrow_forwardGiven the following reversible reactions and Kc values: (I) Self-ionization of water: H2O + H2O H3O+ + OH-, Kc = Kw = 1.0 x 10-14. (II) Ionization of a weak base: NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH-, Kc (= Kb) = 1.8 x 10-5. a) Determine the Kc for the reaction: NH3 + H3O+ NH4+ + H2O b) Would you assess the Kc value as LARGE or small? Does your assessment make sense for this reaction, i.e. think about the species involved?arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the predominant form (principal species) of 1,3-dihydroxybenzene at pH 9.00 and at pH 11.00. What is the second most prominent species at each pH?arrow_forward
- What is the property of Al(OH)3 which, when reacting with organic dyes, serves as confirmatory test?arrow_forwardConsider the following compounds that vary from nearly nonacidic to strongly acidic. Draw the conjugate bases of these compounds, and explain why the acidity increases so dramatically with substitution by nitro groups.CH4 CH3NO2 CH2(NO2)2 CH(NO2)3 pKa ≅ 50 pKa = 10.2 pKa = 3.6 pKa = 0.17arrow_forwardThe azo compound shown below has a λmax value of 410 nm. When treated with hydrogen in the presence of palladium on carbon, the λmax changes significantly. Suggest a reason for this observation and predict whether the λmax value increases or decreases.arrow_forward
- the dissociation constant of 0.25 M propanoic acid C2H5COOH is 1.3 × 10-⁵. a) What is the dissociation rate of C2H5COOH in this solution?arrow_forwardWhich of these structures reacts with Br2 in the dark?arrow_forwardIdentify the acid and conjugate base in each reaction. Calculate the pKA for each acid. List them in order from the strongest to weakest acid. The acid-ionization constants, KA, at 25°C are provided for each. C6H5OH + H2O Û H3O+ + C6H5O-, KA = 1.2589254 x 10-10 CH3CO2H + H2O Û H3O+ CH3CO2-, KA = 1.5848 x 10-5 CF6CO2H+H2O Û H3O+ + CF6CO2-, KA = 0.6309arrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


