
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene,
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Alkene:
The IUPAC name for the alkenes is written by replacing the ‘ane’ of
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Alkene: Unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one double bond between two carbon atoms are known as alkenes.
The IUPAC name for the alkenes is written by replacing the ‘ane’ of alkanes to ‘ene’. The number shoul be in such a way that the alkene carbon gets the low number.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
- (1) Substituted benzenes are named using ‘-benzene’ as the parent.
- (2) When benzene has more than one substituent, the position of those substituents is indicated by numbers or by ortho(o-), meta(m-) or para(p-).
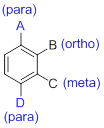
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Alkene: Unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one double bond between two carbon atoms are known as alkenes.
The IUPAC name for the alkenes is written by replacing the ‘ane’ of alkanes to ‘ene’. The number shoul be in such a way that the alkene carbon gets the low number
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Alkyne: Unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms are known as alkynes.
The IUPAC name for the alkynes is written by replacing the ‘ane’ of alkanes to ‘yne’. The number shoul be in such a way that the alkyne carbon gets the low number
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First

 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



