
The data in the table are for the reaction of NO and O2 at 660 K.
NO(g) + ½ O2(g) → NO2(g)
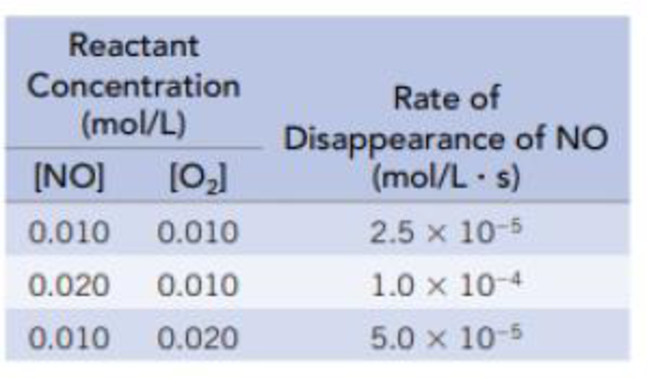
- (a) Determine the order of the reaction for each reactant.
- (b) Write the rate equation for the reaction.
- (c) Calculate the rate constant.
- (d) Calculate the rate (in mol/L · s) at the instant when [NO] = 0.015 mol/L and [O2] = 0.0050 mol/L.
- (e) At the instant when NO is reacting at the rate 1.0 × 10−4 mol/L · s, what is the rate at which O2 is reacting and NO2 is forming?
(a)
Interpretation:
The order of the reaction for each reactant has to be determined
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
Answer to Problem 11PS
The order of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction rate of the chemical reaction is given as,
In order to figure out the reaction equation the order of the reactants needed, which is calculated by comparing any two experiments where the concentration of
(b)
Interpretation:
The rate equation for the reaction has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
Answer to Problem 11PS
The rate equation is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction rate is given as,
Hence, Rate equation is
(c)
Interpretation:
The rate constant has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
Answer to Problem 11PS
The value of rate constant is
Explanation of Solution
The rate constant is calculated as,
The rate constant value is obtained as shown above. By substituting the any one of the concentrations of reactants and the initial rate into the reaction equation obtained at first.
Hence, the value of rate constant is
(d)
Interpretation:
The rate in
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
Answer to Problem 11PS
The instantaneous rate of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The rate is calculated as,
The instantaneous rate of the reaction is
(e)
Interpretation:
The rate at which
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
Answer to Problem 11PS
The rate when oxygen reacting is
Explanation of Solution
The rate is calculated as,
The rate when oxygen reacting is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Organic Chem Lab Survival Manual: A Student's Guide to Techniques
Chemistry: Atoms First
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: Second Semester Topics
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- Express the rate of the reaction 2N2O(g)2N2(g)+O2(g) in terms of (b) [ N2O ] (a) [ O2 ]arrow_forwardAt 573 K, gaseous NO2(g) decomposes, forming NO(g) and O2(g). If a vessel containing NO2(g) has an initial concentration of 1.9 102 mol/L, how long will it take for 75% of the NO2(g) to decompose? The decomposition of NO2(g) is second-order in the reactant and the rate constant for this reaction, at 573 K, is 1.1 L/mol s.arrow_forwardDiethylhydrazine reacts with iodine according to the following equation: Â (C2H5)2(NH)2(l)+I2(aq)(C2H5)2N2+2HI(aq)The rate of the reaction is followed by monitoring the disappearance of the purple color due to iodine. The following data are obtained at a certain temperature. (a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to diethylhydrazine, iodine, and overall? (b) Write the rate expression of the reaction. (c) Calculate k for the reaction. (d) What must [(C2H5)2] be so that the rate of the reaction is 5.00104mol/Lh when [ I2 ]=0.500M?arrow_forward
- 11.44 A possible reaction for the degradation of the pesticide DDT to a less harmful compound was simulated in the laboratory. The reaction was found to be first order, with k = 4.0 X 10_H s"' at 25°C. What is the half-life for the degradation of DDT in this experiment, in years?arrow_forwardWhen boron trifluoride reacts with ammonia, the following reaction occurs: BF3(g)+NH3(g)BF3NH3(g)The following data are obtained at a particular temperature: (a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to BF3, NH3, and overall? (b) Write the rate expression for the reaction. (c) Calculate k for the reaction. (d) When [ BF3 ]=0.533M and NH3=0.300M, what is the rate of the reaction at the temperature of the experiment?arrow_forwardGiven the following mechanism for a chemical reaction: H2O2+IH2O+IOH2O2+IOH2O+O2+I a Write the overall reaction. b Identify the catalyst and the reaction intermediate. c With the information given in this problem, can you write the rate law? Explain.arrow_forward
- The hydrolysis of the sugar sucrose to the sugars glucose and fructose, C12H22O11+H2OC6H12O6+C6H12O6 follows a first-order rate equation for the disappearance of sucrose: Rate =k[C12H22O11] (The products of the reaction, glucose and fructose, have the same molecular formulas but differ in the arrangement of the atoms in their molecules.) (a) In neutral solution, k=2.11011s1 at 27 C and 8.51011s1 at 37 C. Determine the activation energy, the frequency factor, and the rate constant for this equation at 47 C (assuming the kinetics remain consistent with the Arrhenius equation at this temperature). (b) When a solution of sucrose with an initial concentration of 0.150 M reaches equilibrium, the concentration of sucrose is 1.65107M . How long will it take the solution to reach equilibrium at 27 C in the absence of a catalyst? Because the concentration of sucrose at equilibrium is so low, assume that the reaction is irreversible. (c) Why does assuming that the reaction is irreversible simplify the calculation in pan (b)?arrow_forwardSucrose, a sugar, decomposes in acid solution to give glucose and fructose. The reaction is first-order in sucrose, and the rate constant at 25 C is k = 0.21 h1. If the initial concentration of sucrose is 0.010 mol/L, what is its concentration after 5.0 h?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





