
(a)
Interpretation:
To interpret the average power usage
Concept introduction:
The fuel cell operates at voltage of
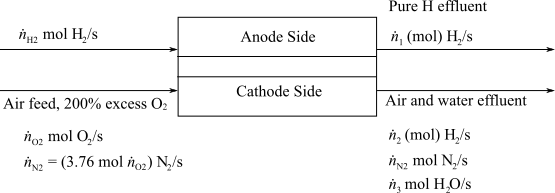
Here,
(b)
Interpretation:
To interpret the flowrates of Hydrogen and Air required in
Concept introduction:
The fuel cell operates at voltage of
The constant
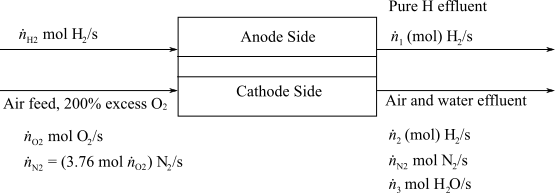
Here,
(c)
Interpretation:
Determine the molar flowrate of Hydrogen exiting from the anode and the molar composition of the cathode exit gas.
Concept introduction:
The fuel cell operates at voltage of
The constant
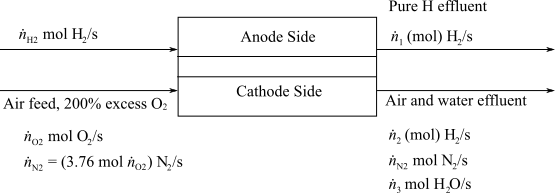
Here,
(d)
Interpretation:
To interpret the number of apartments could be safely powered with a
Concept introduction:
The fuel cell operates at voltage of
The constant
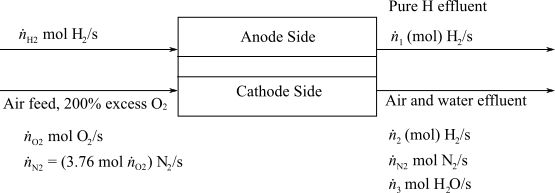
Here,
(e)
Interpretation:
To interpret the times when battery is being charged and the minimum total energy capacity of the battery in
Concept introduction:
The fuel cell operates at voltage of
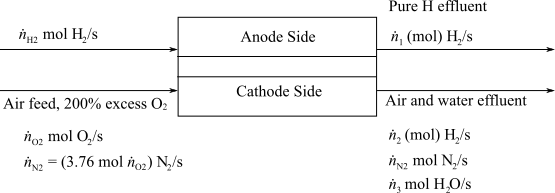
Here,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL P
- Table 17-1 lists common half-reactions along with the standard reduction potential associated with each half-reaction. These standard reduction potentials are all relative to some standard. What is the standard (zero point)? lf is positive for a half-reaction, what does it mean? If is negative for a half-reaction, what does it mean? Which species in Table 17-1 is most easily reduced? Least easily reduced? The reverse of the half-reactions in Table 17-1 are the oxidation half-reactions. How are standard oxidation potentials determined? In Table 17-1, which species is the best reducing agent? The worst reducing agent? To determine the standard cell potential for a redox reaction, the standard reduction potential is added to the standard oxidation potential. What must be true about this sum if the cell is to be spontaneous (produce a galvanic cell)? Standard reduction and oxidation potentials are intensive. What does this mean? Summarize how line notation is used to describe galvanic cells.arrow_forwardAnother step in the metabolism of glucose, which occurs after the formation of glucose6-phosphate, is the conversion of fructose6-phosphate to fructose1,6-bisphosphate(bis meanstwo): Fructose6-phosphate(aq) + H2PO4(aq) fructose l,6-bisphosphate(aq) + H2O() + H+(aq) (a) This reaction has a Gibbs free energy change of +16.7 kJ/mol of fructose6-phosphate. Is it endergonic or exergonic? (b) Write the equation for the formation of 1 mol ADP fromATR for which rG = 30.5 kJ/mol. (c) Couple these two reactions to get an exergonic process;write its overall chemical equation, and calculate theGibbs free energy change.arrow_forwardAG° = 538.7 kJ at 20°C for the reaction: Sg + 12 O2 8 SO3 Calculate E°cel for the reaction in units of mV. mVarrow_forward
- For stationary applications, mass and volume considerations for a fuel source are much less important than they are for use in transportation. It therefore may be the most reasonable to sacrifice compactness to minimize requirements for expensive advanced technologies. Consider a plan to provide power to a small city with a population of 100,000, using hydrogen fuel cells with an efficiency of 60%. The average net per-capita power consumption is 6 kW of electricity, heat, and power for an electric vehicle. (a) Calculate the volume of hydrogen needed to provide the city's energy for one month if the hydrogen is stored at a (relatively low) pressure of 1 MPa. (b) If the city has a land area of 100 km2, what fraction of this area would need to devoted to hydrogen storage if the storage tanks were vertical cylinders 3 m in diameter and 5 m high and were packed tightly together in a square array?arrow_forward1. Copper is found as the mineral covellite (CuS). The first step in extracting the copper is to dissolve the mineral in nitric acid (HNO3), which oxidizes sulfide to sufate and reduces nitric acid to NO: CuS) + HNO3(aq) → NO(g) + CuSO4 -> Balance this equation using the half- reaction method CHEM GINEE RST YEAR FRANE 6 hraarrow_forwardWhat happens to the chemical energy of a lithium-ion battery as it is discharged topower a laptop computer? Does it increase, decrease, or remain unchanged?arrow_forward
- Modules: BIOS 2018 X C + 14 times 200- Google Sear X G Search Google or type a URL F1 F2 Aktiv Chemistry A student wishes to determine the chloride ion concentration in a water sample at 25 °C using a galvanic cell constructed with a graphite electrode and a half-cell of AgCl(s) + e → Ag(s) + Cl(aq) Eºred = 0.2223 V And a copper electrode with 0.500 M Cu²+ as the second half cell Cu²+ (aq) + 2 e → Cu(s) E°red= 0.337 V The measured cell potential when the water sample was placed into the silver side of the cell was 0.0925 V. 80 F3 Given the standard cell potential for this cell is 0.115 V, and the measured cell potential is 0.0925, what is the concentration of chloride ions in the solution? 000 000 F4 X F5 Google Docs: Online Docur X Google Question 8.d of 16 MacBook Air F6 gaarrow_forwardConsider an electrochemical cell operating under standard conditions and at 25 °C. One half cell is the standard hydrogen electrode and the other contains permanganate ions and manganese(lI) ions in an acidified solution. When the cell operates, the value of A¸G° is a. 1.47 x 106 J Оb.7,33 х 105 J Ос. 2.93 х 105 J Od.. 1.47 x 106 Oe..7.33 x 105 J Of. - 2.93 x 105 Og. None of the above. 8.arrow_forward6) What standard condition(s) the electrochemistry experiment? are violated when using the version of the Nernst equation used inarrow_forward
- . Calculate the Gibbs free energy changes, AG, by using the potential differences measured in Part I and II by using the formula, AG = -nFɛ. n is the number of electrons transferred in the reaction. F is the Faraday's constant and equals to 96500 Coulomb. |3| Total cell reaction: Zn(s) + Cu"(aq) - Zn*(aq) + Cu(s) Part I. 1. Beaker: 0.1 M CUSO4 solution, 2. Beaker: 0.1M ZnSO4 solution. Part II. 1. Beaker: 0.1 M CuSO4 solution, 2. Beaker: 0.01M ZNSO4 solution. 2. Find percent errors for part I and II. The theoretical value of standard cell potential, e, is 1.100 V Cell >arrow_forwardBalance the following reaction in basic solution. Ag(s) + Zn²+(aq) → Ag,O(ag) + Zn(s) Fill in the coefficients and substances for the balanced overall equation. Note: Do NOT leave any coeffient fields empty. If the coefficient is 1, choose "1" as opposed to leaving it blank. -- v Ag + -- v Zn2+ + v Zn + Ag,0 + -- v--arrow_forwardBalance the following equation by selecting the coefficients in the dropdown boxes.The coefficient for C5H12 isa. 1b. 2c. 3d. 4The coefficient for O2 isa. 1b. 2c. 3d. 4e. 5f. 6g. 7h. 8i. 9j. 10The coefficient for CO2 is a. 1b. 2c. 3d. 4e. 5f. 6g. 7h. 8i. 9j. 10The coefficient for H2O is a. 1b. 2c. 3d. 4e. 5f. 6g. 7h. 8i. 9j. 10arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




