
Concept explainers
Interpretation:The manner inhibition of radical chlorination of methane is possible when radical inhibitors such as
Concept introduction:The mechanism for monochlorination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Step 1- Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
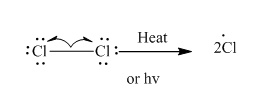
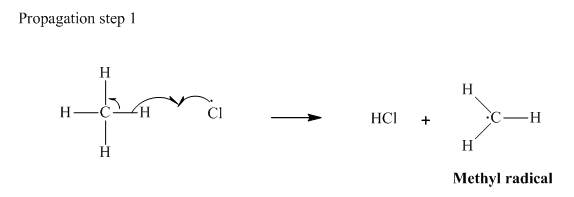
Step 2: Propagation: In the first of the propagation steps,
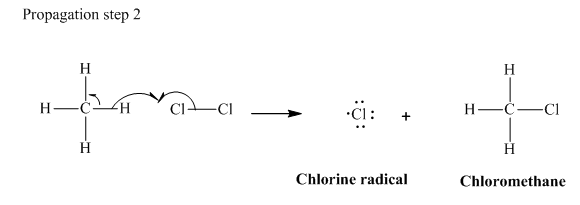
In subsequent propagation step,chloromethyl radical abstracts
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon the combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- As we will learn, many antioxidants–compounds that prevent unwanted radical oxidation reactions from occurring–are phenols, compounds that contain an OH group bonded directly to a benzene ring.a.) Explain why homolysis of the O–H bond in phenol requiresconsiderably less energy than homolysis of the O–H bond in ethanol(362 kJ/mol vs. 438 kJ/mol).b.) Why is the C–O bond in phenol shorter than the C–O bond in ethanol?arrow_forwardUsing the table of average bond dissociation enthalpies at 25°C, determine which of the following reactions are energetically favorable at room temperature. Assume that ▲S = 0. Q. CH2=CH2 + (CH3)3SiH --> CH3CH2Si(CH3)3arrow_forwardDefine the Mechanism of the Radical Addition of HBr to an Alkene ?arrow_forward
- What reaction would acetylene likely undergo if it were kept at 1500 °C for too long?9arrow_forwardThe rate law for addition of Br2 to an alkenes is first order in Br2 and first order in the alkene. Does this information suggest that the mechanism of addition of Br2 to an alkene proceeds in the same matter as for addition of HBr? Explain.arrow_forwardAlkyl halides can be reduced to alkanes by a radical reaction with tributyltin hydride, (C4H9)3SnH, in the presence of light (hv). Propose a radical chain mechanism by which the reaction might occur. The initiation step is the light-induced homolytic cleavage of the Sn-H bond to yield a tributyltin radical.arrow_forward
- If 0.70 g of FeCl3 is used to iodinate 8.42 g of benzene with sufficient ICl, what is the average number of reactions that each FeCl3 molecule must catalyze?arrow_forwardWhat is the heat of combustion of ethane, C2H6, in kilojoules per mole of ethane? Properties of C2H6 at 298K ∆Hf °kJ/mol = –84.0 ∆Gf°kJ/mol –32.0 S°J/(mol·K) = 229.2 Δ?∘rxn=___________kJ/mol ethanearrow_forward# moles of c2h2 that will burn in the presence of 1.43 mol o2?arrow_forward
- Does increasing the energy barrier for an SN2 reaction increase or decrease the magnitude of the rate constant for the reactionarrow_forward1-Suggest a mechanism by which the ozone, O3 is being destructed by the presence of oxygen molecule, O2, and the sun light. 2-Methyl chloride, CH3Cl, is another molecule that destructs the ozone layer. Suggest a mechanism for the destruction of ozone by methyl chloride and the sun light.arrow_forwardThe standard enthalpies of formation of ClO and ClO2 are101 and 102 kJ/mol, respectively., Calculate the overallenthalpy change for each step in the following catalyticcycle: What is the enthalpy change for the overall reaction thatresults from these two steps? ClO(g) + O3(g) ---->ClO2(g) + O2(g) ClO2(g) + O(g) ---->ClO(g) + O2(g)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning


