
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.

Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
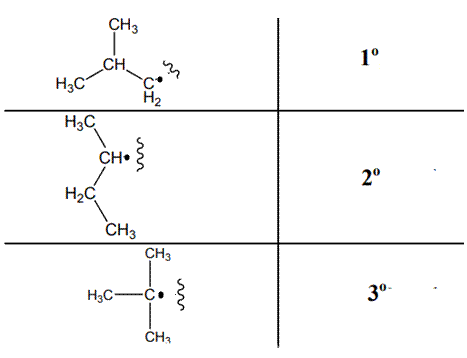
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(b)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
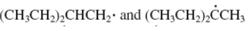
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
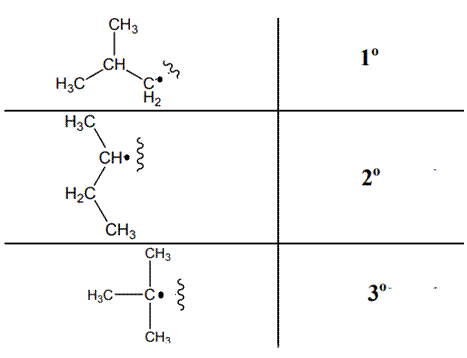
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(c)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
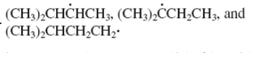
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
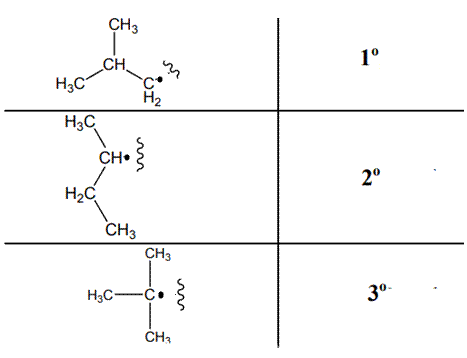
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyper conjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Draw resonance forms to show how the BHA radical is stabilized by delocalization of the radical electron over other atoms in the molecule.arrow_forwarddraw the two possible carbocations that can form when this alkene reacts with a strong acid (such as HBr or H3O+). of the two structures you drew, circle the more stable carbocationarrow_forwardDraw cis and trans 1,2-dichloroethylene (C2H2Cl2) and predict their relative energiearrow_forward
- Assign the hydrogens in C7H14O to this structurearrow_forwardWrite the propagation steps leading to the formation of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) from chloromethanearrow_forwardWhen free radical halogenation is performed with one of the compounds below, only a single product with the formula C5H11Cl is isolated. Which compound fits this description? Select one: a. 2,2-dimethylpropane b. cyclopentane c. pentane d. 2-methylbutanearrow_forward
- 2-chloropropane is a major product of the reaction of chlorine with propane under ultraviolet light. Write the mechanism for this reaction including the initiation step and the two propagation steps.arrow_forwardFrom studies of the dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane in the gas phase at room temperature (25°C), it is estimated that the ratio of molecules in the anti conformation to gauche conformation is 7.6 to 1. Calculate the difference in Gibbs free energy between these two conformations.arrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions. cyclopentadiene + methyl acrylate, CH2“CH¬COOCH3arrow_forward
- Acetonitrile (CH3CN) has resonance at 1.97 ppm, whereas methyl chloride (CH3Cl) has resonance at 3.05 ppm, even though the dipole moment of acetonitrile is 3.92 D and that of methyl chloride is only 1.85 D. The larger dipole moment for the cyano group suggests that the electronegativity of this group is greater than that of the chlorine atom. Explain why the methyl hydrogens on acetonitrile are actually more shielded than those in methyl chloride, in contrast with the results expected on the basis of electronegativityarrow_forwardWhich is more stable - a phenyl radical, [C6H5]•, or a benzyl radical, [C6H5CH2]• - and why?arrow_forwardThe pentadienyl radical, H2C“CH¬CH“CH¬CH2#, has its unpaired electron delocalized over three carbon atoms. How many nodes are there in the lowest-energy MO of the pentadienyl system? How many in the highest-energy MO?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



