
Methanol is synthesized from carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the reaction
A process ?owchart is shown below.
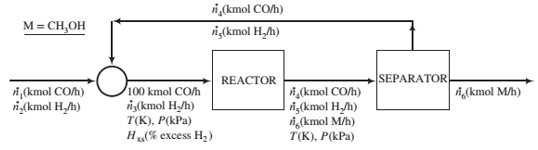
The fresh feed to the system, which contains only CO and H2, is blended with a recycle stream containing the same species. The combined stream is heated and compressed to a temperature T(K) and a pressure P(kPa) and fed to the reactor. The percentage excess hydrogen in this stream is Hxs. The reactor ef?uent—also at T and P—goes to a separation unit where essentially all of the methanol produced in the reactor is condensed and removed as product. The unreacted CO and H2constitute the recycle stream blended with the fresh feed.
Provided that the reaction temperature (and hence the rate of reaction) is high enough and the ideal- gas equation of state is a reasonable approximation at the reactor outlet conditions (a questionable assumption), the ratio
In these equations, piis the partial pressure of species i in kilopascals
Suppose P = 5000 kPa, T = 500 K, and the percentage excess of hydrogen in the feed to the reactor (Hxs) = 5.0%. Calculate
- ) and the ?ow rate (SCMH) of the recycle stream.
Run the program for the following nine conditions (three of which are the same):
(c) You should ?nd that the methanol yield increases with increasing pressure and decreasing temperature. What cost is associated with increasing the pressure?
(d) Why might the yield be much lower than the calculated value if the temperature is too low?
(e) If you actually ran the reaction at the given conditions and analyzed the reactor ef?uent, why might the spreadsheet values in Columns F—M be signi?cantly different from the measured values of these quantities? (Give several reasons, including assumptions made in obtaining the spreadsheet values.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Process Dynamics and Control, 4e
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Edition) (Prentice Hall International Series in the Physical and Chemical Engineering Sciences)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Starting Out with Python (3rd Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
- 4.64. The gas-phase reaction between methanol and acetic acid to form methyl acetate and water CH;OH + CH3COOH = CH3COOCH3 + H2O (A) (В) (C) (D) takes place in a batch reactor. When the reaction mixture comes to equilibrium, the mole fractions of the four reactive species are related by the reaction eqilibrium constant Ky : = 4.87 YAYB (a) Suppose the feed to the reactor consists of n40,NB0, NCo, NDO, and no gram-moles of A, B, C, D, and an inert gas, I, respectively. Let į be the extent of reaction. Write expressions for the gram-moles of each reactive species in the final product, nA(2), nB(3), nc(E), and np(3). Then use these expressions and the given equilibrium constant to derive an equation for , the equilibrium extent of reaction, in terms of n20,.., N1o. (see Example 4.6-2.) (b) If the feed to the reactor contains equimolar quantities of methanol and acetic acid and no other species, calculate the equilibrium fractional conversion. (c) It is desired to produce 70 mol of methyl…arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction CS2(g) + 3O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2SO2(g) A mixture containing only CS2(g) and excess O2(g) at a total pressure of 100 kPa is placed in a sealed vessel. After the reaction is completed and the vessel is cooled to the initial temperature, the total pressure in the vessel drops to 80 kPa. What is the mole fraction of CO2(g) in the final mixture?arrow_forwardWhen the following gas reaction reaches equilibrium, at a certain temperature, the moles fractions of the four reactive species satisfy the following relation (we will use "y" for mole fractions since all of these reagents and products are gases): CO+H20 > CO2+H2 [yCO2][yH2] K= [yC0][YH20] Where K= 1. Assume that the feed introduced to the reactor is 2 mol of CO and 4 mol of H20 only. Also assume that the reaction reaches equilibrium. need to calculate the mole fraction for all a) Calculate the equilibrium composition, for this reactants and products. Answer: yCo2 = 2/9 = 2/9 yH2 УСо - 1/9 YH2O = 4/9|arrow_forward
- When the following gas reaction reaches equilibrium, at a certain temperature, the moles fractions of the four reactive species satisfy the following relation (we will use "y" for mole fractions since all of these reagents and products are gases): CO+H20 CO2+H2 K= [yCO2][yH2] [yco][yH20] Where K= 1. Assume that the feed introduced to the reactor is 2 mol of CO and 4 mol of H20 only. Also assume that the reaction reaches equilibrium. a) Calculate the extent of reaction in equilibrium (Šeg) b) Calculate the equilibrium composition, for this you need to calculate the mole fraction for all reactants and products.arrow_forwardFor the reaction bellow: C„H(2n+2) + a(02 + 3.76 N2) → nC02 + (n+ 1)H,0 + 3.76a N2 If the heat of combustion writing as: Qc = 618.49 n+ 187. 83 And the mole fraction of CO, in products is Xco, 1. Type of fuel. 2. Heat of combustion (KJ/mole of fuel) 25 find: 227 3. If n=4, find the mole fractions of Co, H,0 and N2arrow_forwardA mixture of isobutylene ((CH3)2CCH2, 0.400 bar partial pressure) and HCI (0.600 bar partial pressure) is heated at 500.0 K. The equilibrium constant K for the gas- phase thermal decomposition of tert- butyl chloride ((CH3)3CCI) is 3.45 at 500.0 K. bar (CH3);CCI(g) = (CH3)2CCH2(g) + HCI(g) 1 3 What is the partial pressure of isobutylene ((CH3)2CCH2) at equilibrium? 4 C 8. 9. +/- х 100arrow_forward
- A mixture of isobutylene ((CH3)2CCH2, 0.400 bar partial pressure) and HCI (0.600 bar partial pressure) is heated at 500.0 K. The equilibrium constant K for the gas- phase thermal decomposition of tert- butyl chloride ((CH3)3CCI) is 3.45 at 500.0 K. bar (CH3);CCI(g) = (CH3)2CCH2(g) + HCI(g) 1 3 What is the partial pressure of hydrochloric acid (HCI) at equilibrium? 4 C 8. 9. +/- х 100arrow_forwardA mixture of isobutylene ((CH3)2CCH2, 0.400 bar partial pressure) and HCI (0.600 bar partial pressure) is heated at 500.0 K. The equilibrium constant K for the gas- phase thermal decomposition of tert- butyl chloride ((CH3)3CCI) is 3.45 at 500.0 K. bar (CH3);CCI(g) = (CH3)2CCH2(g) + HCI(g) 1 3 You have calculated the equilibrium partial pressures to be: 4 C tert-butyl chloride,CH3);CCI = (x) hydrochloric acid, HCI = (0.600 - x) isobutylene, (CH3)2CCH2 = (0.400 - x) What is the partial pressure of tert- butyl chloride ((CH3)3CCI) at equilibrium? 8. 9. +/- х 100arrow_forwardCa(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(8) + 2H2O(1) 2. Standar... 1req For the reaction 3. AS surrou... 1req 4. AG° = A... 1req 5. AG: Pre... 1req 6. AG: Enthal... M 7. AG fro... 1req 8. Calculat... 1req 9. Calculat... 1req Question Question Question 10. Calcul... 1req AH° 30.2 kJ and AS° = 206 J/K The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 280.0 K is Assume that AH° and As are independent of temperature. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 3 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- The n-butane is converted into isobutane in an isomerization reactor, which operates isothermally at 149°C. Suppose that the reactor is fed with a mixture containing 93% mole of n-butane, 5% isobutane and 2% HCl at 149°C and that a 40% conversion of n-butane is achieved. How much heat in KJ/m3 (STP) of the feed, should be supplied or extracted from the reactor?arrow_forwardDetermine the volume (L) of hydrogen needed (based on room temperature 25 °C and l atm) to hydrotreat 1 liter crude oil with 1.8 wt % S to a sulfur content of 0.2 wt%. The oil has a specific gravity of 0.8 (compared to water). The stoichiometry follows the following reaction: Oil-S + 2H2¬→O¡I-H2 + H2Sarrow_forward(b) The condensation reaction of acetone (CH3)2CO in aqueous solution is catalysed by base B, which reacts reversibly with acetone to form the carbion, C3H50¯. The carbion then reacts with a molecule of acetone to give product P АН BH A k.1 A НА P k2 AH = acetone A= carbion B= base catalyst (i) Use steady state approximation to determine the concentration of the carbion and hence derive the rate equation for the formation of product, P.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





